Topic: Eccentricity Rate Gradient Standard Error
Eccentricity Rate Gradient Standard Error
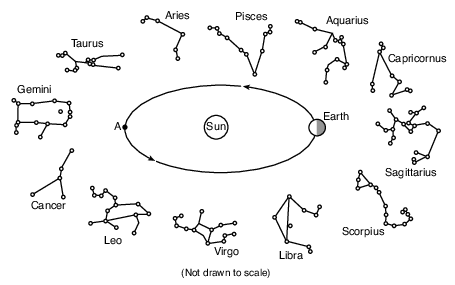
Approximately how many days (d) does it take for Earth to orbit from its present position to point A?
(1) 27 d
(2) 91 d
(3) 183 d
(4) 365 d
Due to radioactive decay, an igneous rock sample now contains one-fourth of the amount of potassium-40 that it originally contained. The age, in years, of this rock sample is approximately
(1) 0.7 109 y
(2) 1.3 109 y
(3) 2.6 109 y ×× ××
(4) 5.2 109 y
What is the approximate density of a mineral with a mass of 262.2 grams that displaces 46 cubic centimeters of water?
(1) 1.8 g/cm3
(2) 5.7 g/cm3
(3) 6.1 g/cm3
(4) 12.2 g/cm3
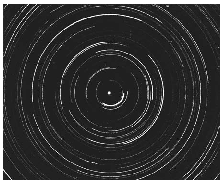
During the time exposure of the photograph, the stars appear to have moved through an arc of 120°. How many hours did this time exposure take?
(1) 5 h
(2) 8 h
(3) 12 h
(4) 15 h
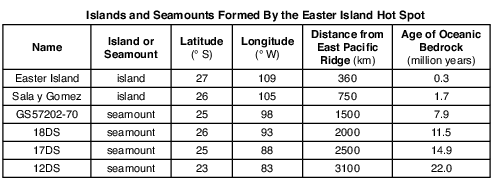
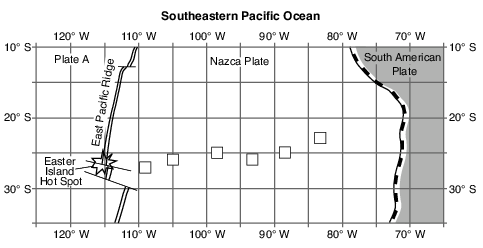
On the map in the image provided, plot with Xs the locations of the six islands and seamounts formed by the Easter Island Hot Spot. [1]
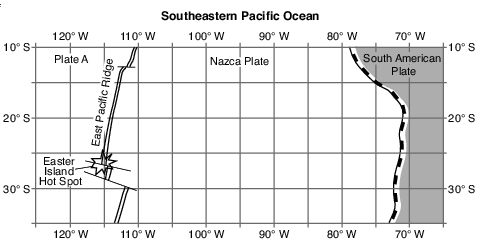
Allow 1 credit if the centers of all six Xs are within or touch the clear boxes shown below.. Note: Allow credit if a symbol other than an X is used.
• It is recommended that an overlay of the same scale as the student answer sheet be used to ensure reliability in rating.
• 
On the grid in the image provided, construct a topographic profile along line AB by plotting the elevation of each contour line that crosses line AB. The elevations of points A and B have been plotted on the grid. Connect all nine plots with a line from A to B to complete the profile. [1]

Allow 1 credit if the centers of all seven student plots are within or touch the clear rectangles shown below and all nine plots are correctly connected with a line that passes within or touches the rectangles. The line must show the highest elevation above 640 m, but below 660 m.
• Note: Allow credit if the line does not pass through the student’s plots, but is still within or
• touches the rectangles.
• It is recommended that an overlay of the same scale as the student answer sheet be used to ensure reliability in rating.
• 
On the timeline in the image below, accurately shade in an area to represent the entire Permian Period. [1]
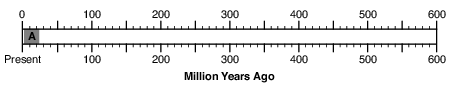
Allow 1 credit for a shaded bar that begins and ends within or is touching the clear rectangles shown below.
• 
•
• Note: It is recommended that an overlay of the same scale as the student answer sheet be used
• to ensure reliability in rating.
Calculate the gradient along line CD and label your answer with the correct units. [1]
Gradient =
Allow 1 credit for any value from 23 to 27 with the correct units. Acceptable units include, but are not limited to:
• — feet/mile
• — ft per mi
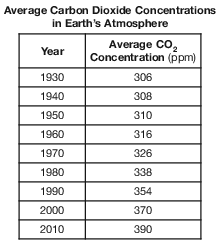
On the grid in the image below, construct a line graph by plotting the average carbon dioxide concentrations in Earth’s atmosphere for each year shown on the data table. Connect the plots with a line. [1]

Allow 1 credit if all nine plots are within the circles shown below and are connected with a line that passes within the circles.
• Note: It is recommended that an overlay of the same scale as the student answer booklet be used
• to ensure reliability in rating.
• 
Huygens Probe Lands on Titan
The Huygens probe was carried to Saturn by the Cassini spacecraft and parachuted to the surface of Saturn’s giant moon, Titan. The Huygens probe’s landing site was littered with smooth, rounded, rocklike objects. Photographs taken of Titan’s surface show drainage channels leading to an apparent shoreline. The question is, what are they draining? One of the photographs seems to show ground fog consisting not of water, but perhaps of ethane or methane.

Approximately how many times farther is Titan from Saturn than Earth’s Moon is from Earth? [1]
times farther
Allow 1 credit for any value from 3.0 to 3.2 times farther.
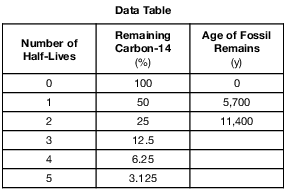
The carbon-14 in the fossil remains of a mastodont has undergone five half-lives of radioactive decay. Calculate the age of these fossil remains. [1]
y
Allow 1 credit for 28,500 y.
Foucault’s Pendulum
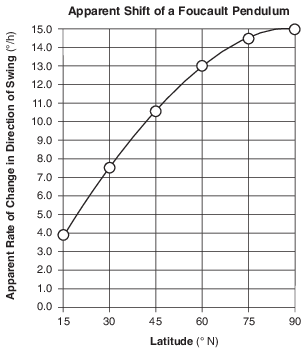
In 1851, Jean-Bernard-Léon Foucault attached a heavy iron ball to a steel wire hanging from the high ceiling of a church in Paris to demonstrate an apparent motion caused by Earth’s rotation. This pendulum could swing freely back and forth. A spike on the bottom of Foucault’s pendulum produced straight lines in sand spread on the floor. The position of each new line appeared to gradually shift in a clockwise direction. Eventually, the pendulum returned to its original path, completing a 360° pattern in approximately 32 hours. At other northern latitudes, a Foucault pendulum will complete a 360° pattern of swing in different amounts of time. In the Northern Hemisphere, the number of degrees that a pendulum appears to change its clockwise direction of swing each hour varies with latitude.
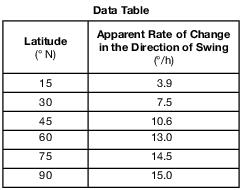
On the grid in the image provided, plot the apparent rate of change in a Foucault pendulum’s direction of swing for each of the latitudes given in the data table. Connect the plots with a line. [1]
Allow 1 credit if the centers of all six plots are within or touch the circles shown and the plots are correctly connected with a line that passes within or touches the circles.
• Note: Allow credit if the student-drawn line does not pass through the student plots, but is still
• within or touches the circles.. It is recommended that an overlay of the same scale as the student answer booklet be used to ensure reliability in rating.
• 
The star Canopus has a surface temperature of 7400 K and a luminosity (relative to the Sun) of 1413. In your answer booklet, use an X to plot the position of Canopus on the graph, based on its surface temperature and luminosity. [1]
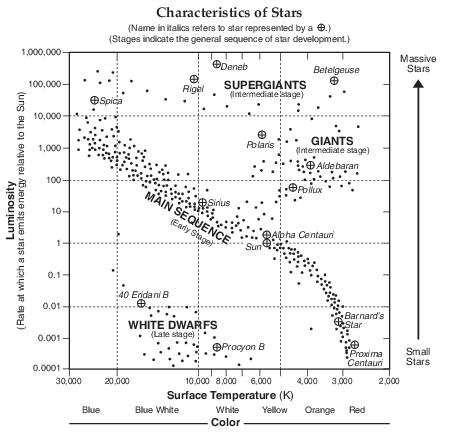
Allow 1 credit if the center of the X is placed within or touches the box shown below.
• Note: Allow credit if a symbol other than an X is used.
• It is recommended that an overlay of the same scale as the student answer booklet be used to ensure reliability in rating.
• 
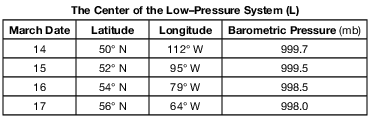
On the map in the image provided, use the latitudes and longitudes listed in the data table to plot the March 16 and March 17 locations of the center of the low-pressure system (L) by placing an X at each location. [1]
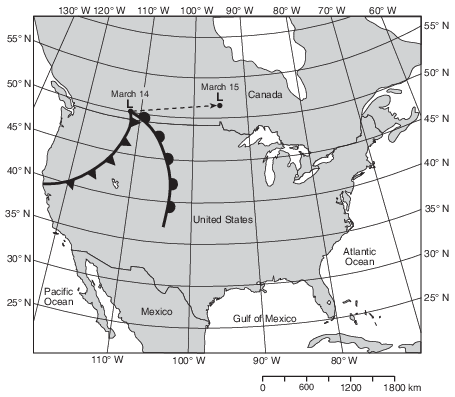
Allow 1 credit if the centers of the two Xs fall within or touch the two empty boxes shown below.
• Note: Allow credit if a symbol other than an X is used.
• It is recommended that an overlay of the same scale as the student answer booklet be used to ensure reliability in rating.
• 

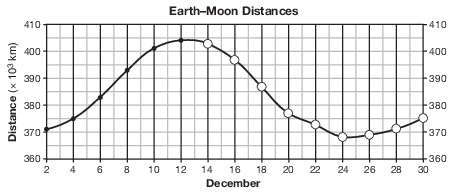
On the grid in the image provided, the Earth–Moon distance data from December 2 to December 12 have already been plotted. Complete the line graph by plotting the Earth–Moon distances from December 14 to December 30. Continue the line from December 12 through all nine of your plotted points. [1]
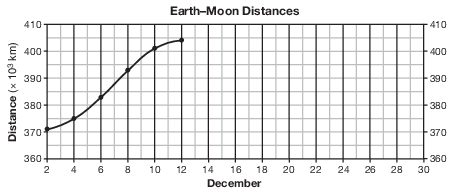
Allow 1 credit if the centers of all nine of the student’s plots are within or touch the circles shown and all 15 plots are correctly connected with a line that passes within or touches each circle.
• Note: Allow credit if the line misses a plot but is still within or touches the circle.
• It is recommended that an overlay of the same scale as the student answer booklet be used to ensure reliability in rating.
•